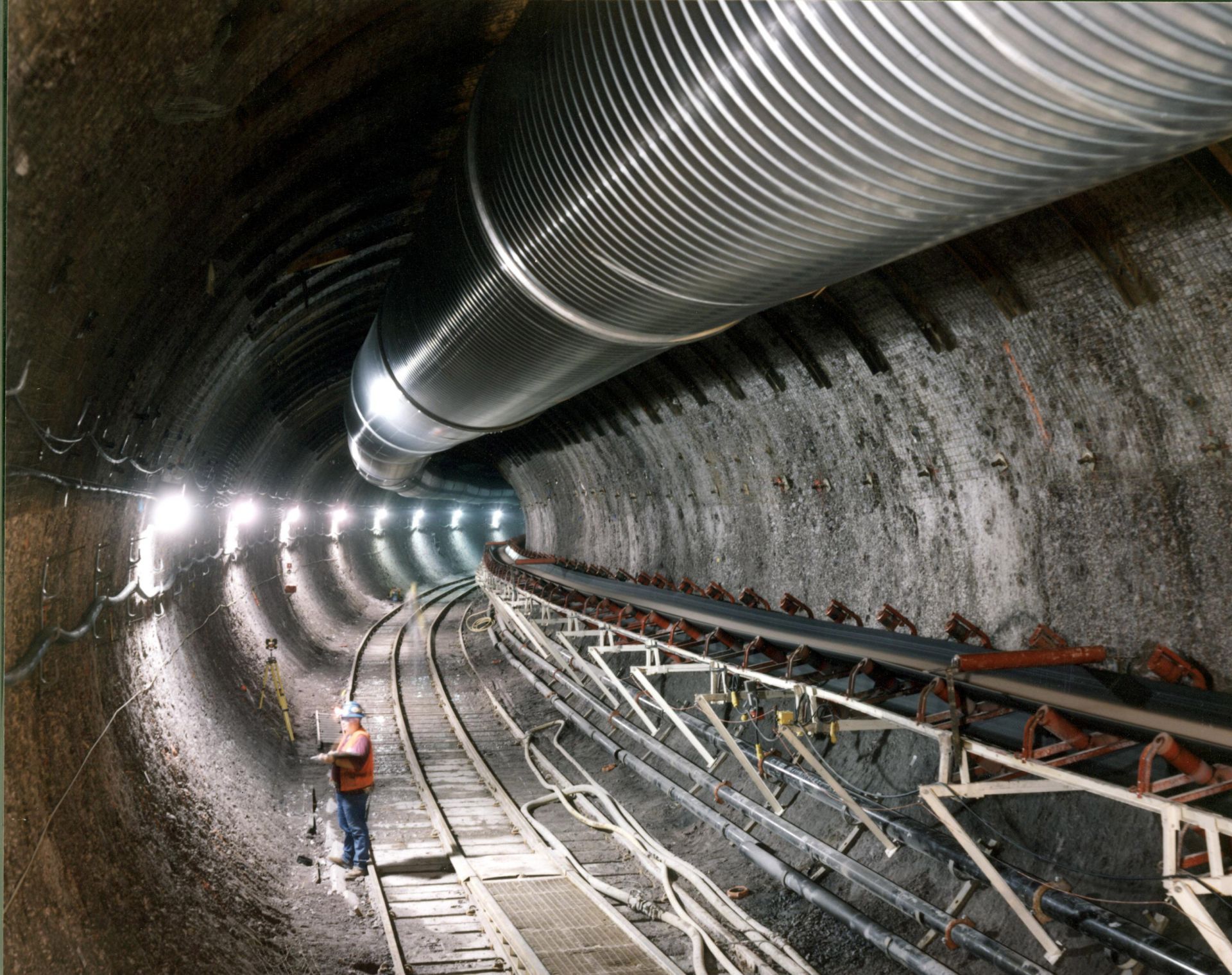
February 17, 2023, 3:03PMRadwaste SolutionsPeter Swift, Michael Apted, Lake Barrett, John Kessler, and Steven Nesbit An electric continuous miner machine cuts out a waste-emplacement panel at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant salt repository in New Mexico. (Photo: DOE)
Used nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes are by-products of nuclear energy production and other applications of nuclear technology, and the consensus approach to disposing of those wastes safely is to encapsulate them and emplace them in stable geologic formations (geologic repositories) where they will be isolated from people and the environment for very long periods of time. The federal government has established environmental standards for waste isolation that any proposed geologic repository must meet.
In July 2021, the American Nuclear Society established a special committee to consider possibilities for revised generic environmental standards for disposal of spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste in the United States. The committee developed a number of recommendations, which are contained in a draft report that was to be issued in February for review and comment by stakeholders. The draft report can be found on the ANS website, at ans.org/policy/repositorystandard/.
The committee’s draft recommendations are based on two underlying assumptions. First, that the relevant legislative framework for regulation defined in the Nuclear Waste Policy Act (NWPA) remains unchanged. Specifically, it is assumed that the Environmental Protection Agency will be charged with promulgating environmental standards for disposal and that the Nuclear Regulatory Commission will be charged with reviewing applications for disposal facilities using licensing requirements and criteria consistent with the EPA standards. Second, that existing generic disposal standards will be updated or replaced.
NWMO geologists study rock formations in the Ignace area of Ontario, Canada.
Canada’s Nuclear Waste Management Organization is studying the geology of the Ignace, Ontario, area to confirm its suitability as a site for a deep geologic repository for spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste. Ignace is one of two areas the NWMO is investigating as possible host sites for a repository, with South Bruce, Ontario, being the second area.
The underground Exploratory Studies Facility at Yucca Mountain in Nevada built by the Department of Energy to determine whether the location was suitable as a deep geological nuclear waste repository. Courtesy of the Department of Energy.
It is no secret that the U.S. government’s program to manage and dispose of used nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste is in a deep ditch. Private companies continue to safely store used fuel at U.S. nuclear reactor sites, some of which ceased power operations decades ago. Other countries, such as Finland, Sweden, France, Canada, Switzerland, Russia, and China, are moving forward on permanent disposal, while for the past 11 years, the U.S. government has done nothing constructive to discharge its HLW disposal responsibilities. Rather than taking action, successive Congresses and administrations have sat on their collective hands.
A retired USGS geologist shares his experience of working on the publicly misunderstood nuclear waste repository and its geology.
The author on a typical day at Yucca Mountain, with Solitario Canyon and the flat-topped repository block seen in the background.